How To Use Excel To Make A Graph
Charts help yous visualize your data in a way that creates maximum impact on your audience. Larn to create a chart and add a trendline. You can start your document from a recommended nautical chart or choose one from our collection of pre-congenital nautical chart templates.

Create a nautical chart
-
Select data for the chart.
-
SelectInsert >Recommended Charts.
-
Select a chart on theRecommended Charts tab, to preview the nautical chart.
Note:Y'all tin can select the information you desire in the chart and press ALT + F1 to create a chart immediately, but it might non exist the best chart for the data. If you don't see a chart you like, select theAll Charts tab to see all chart types.
-
Select a chart.
-
SelectOK.
Add a trendline
-
Select a nautical chart.
-
SelectDesign >Add Chart Element.
-
SelectTrendline and then select the type of trendline you desire, such as Linear, Exponential, Linear Forecast, orMoving Boilerplate.
Annotation:Some of the content in this topic may not be applicable to some languages.
Charts display data in a graphical format that can help yous and your audition visualize relationships between data. When you lot create a nautical chart, you can select from many nautical chart types (for example, a stacked column chart or a iii-D exploded pie chart). After you lot create a chart, you tin customize it by applying chart quick layouts or styles.
Charts comprise several elements, such as a title, centrality labels, a fable, and gridlines. You lot can hide or display these elements, and you tin also modify their location and formatting.
 Chart title
Chart title
 Plot area
Plot area
 Legend
Legend
 Axis titles
Axis titles
 Axis labels
Axis labels
 Tick marks
Tick marks
 Gridlines
Gridlines
You lot can create a nautical chart in Excel, Word, and PowerPoint. Even so, the chart data is entered and saved in an Excel worksheet. If you insert a chart in Give-and-take or PowerPoint, a new sheet is opened in Excel. When you relieve a Word certificate or PowerPoint presentation that contains a chart, the chart'south underlying Excel information is automatically saved within the Word document or PowerPoint presentation.
Notation:The Excel Workbook Gallery replaces the former Chart Wizard. By default, the Excel Workbook Gallery opens when you open Excel. From the gallery, yous tin can browse templates and create a new workbook based on one of them. If you don't see the Excel Workbook Gallery, on the File menu, click New from Template.
-
On the View carte du jour, click Print Layout.
-
Click the Insert tab, and and so click the pointer side by side to Chart.
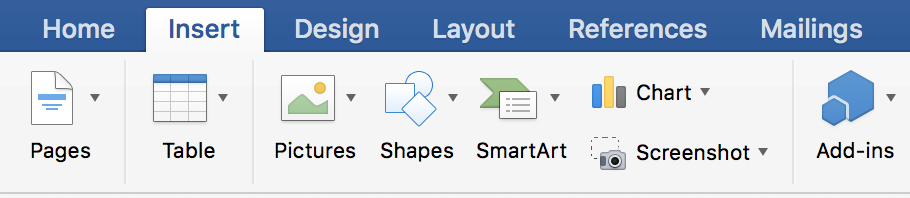
-
Click a chart type, and then double-click the chart you desire to add.
When you insert a nautical chart into Word or PowerPoint, an Excel worksheet opens that contains a table of sample data.
-
In Excel, supervene upon the sample data with the information that you lot want to plot in the chart. If you lot already have your information in another table, you tin can copy the data from that table and so paste information technology over the sample data. See the following tabular array for guidelines for how to adjust the data to fit your chart type.
For this chart type
Arrange the data
Surface area, bar, column, doughnut, line, radar, or surface chart
In columns or rows, as in the following examples:
Serial 1
Series 2
Category A
ten
12
Category B
11
14
Category C
9
15
or
Category A
Category B
Serial 1
10
11
Series 2
12
xiv
Bubble nautical chart
In columns, putting x values in the get-go column and respective y values and bubble size values in adjacent columns, as in the following examples:
Ten-Values
Y-Value 1
Size 1
0.7
two.seven
iv
1.8
iii.2
v
two.6
0.08
6
Pie chart
In 1 cavalcade or row of data and one column or row of data labels, as in the following examples:
Sales
1st Qtr
25
2nd Qtr
xxx
third Qtr
45
or
1st Qtr
second Qtr
3rd Qtr
Sales
25
xxx
45
Stock chart
In columns or rows in the following society, using names or dates equally labels, every bit in the following examples:
Open up
High
Low
Shut
1/5/02
44
55
11
25
one/6/02
25
57
12
38
or
1/5/02
1/6/02
Open up
44
25
Loftier
55
57
Depression
11
12
Close
25
38
X Y (scatter) chart
In columns, putting x values in the first cavalcade and corresponding y values in next columns, every bit in the following examples:
X-Values
Y-Value 1
0.seven
2.7
1.8
3.2
2.six
0.08
or
X-Values
0.seven
one.8
two.6
Y-Value one
2.7
three.two
0.08
-
To modify the number of rows and columns included in the chart, balance the arrow on the lower-correct corner of the selected data, and then elevate to select boosted information. In the post-obit case, the table is expanded to include additional categories and data series.
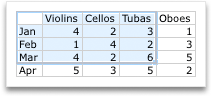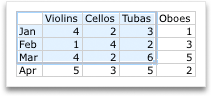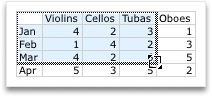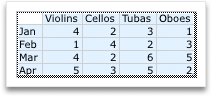
-
To see the results of your changes, switch back to Word or PowerPoint.
Note:When you close the Word document or the PowerPoint presentation that contains the chart, the chart'south Excel data table closes automatically.
After yous create a chart, you lot might want to alter the way that table rows and columns are plotted in the chart. For case, your offset version of a chart might plot the rows of data from the table on the chart'southward vertical (value) axis, and the columns of data on the horizontal (category) axis. In the post-obit example, the chart emphasizes sales past instrument.
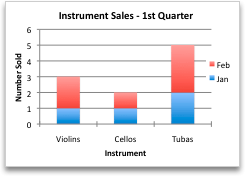
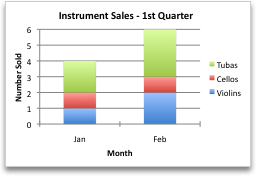
Even so, if you want the nautical chart to emphasize the sales by month, yous can contrary the style the chart is plotted.
-
On the View menu, click Print Layout.
-
Click the nautical chart.
-
Click the Chart Design tab, and so click Switch Row/Cavalcade.
If Switch Row/Cavalcade is not available
Switch Row/Column is available only when the chart's Excel data table is open up and only for certain chart types. You tin can also edit the data by clicking the chart, so editing the worksheet in Excel.
-
On the View menu, click Print Layout.
-
Click the chart.
-
Click the Nautical chart Pattern tab, and then click Quick Layout.
-
Click the layout you want.
To immediately undo a quick layout that you practical, press
 + Z .
+ Z .
Chart styles are a ready of complementary colors and effects that you can apply to your chart. When you select a chart style, your changes bear upon the whole chart.
-
On the View menu, click Print Layout.
-
Click the chart.
-
Click the Chart Design tab, and then click the manner you desire.
To run across more styles, bespeak to a style, and then click
 .
.To immediately undo a style that you applied, press
 + Z .
+ Z .
-
On the View menu, click Print Layout.
-
Click the chart, and and so click the Chart Pattern tab.
-
Click Add Chart Element.

-
Click Chart Title to cull title format options, and then return to the nautical chart to type a title in the Chart Title box.
See also
Update the data in an existing chart
Chart types
You can create a nautical chart in Excel, Give-and-take, and PowerPoint. However, the chart data is entered and saved in an Excel worksheet. If you insert a chart in Word or PowerPoint, a new sheet is opened in Excel. When yous save a Discussion document or PowerPoint presentation that contains a chart, the nautical chart'south underlying Excel data is automatically saved within the Discussion document or PowerPoint presentation.
Notation:The Excel Workbook Gallery replaces the former Chart Wizard. By default, the Excel Workbook Gallery opens when you open up Excel. From the gallery, you can browse templates and create a new workbook based on one of them. If you don't encounter the Excel Workbook Gallery, on the File menu, click New from Template.
-
On the View card, click Print Layout.
-
On the Charts tab, nether Insert Nautical chart, click a chart blazon, and so click the 1 that you want to add together.
When yous insert a chart into Word or PowerPoint, an Excel canvass opens that contains a tabular array of sample information.
-
In Excel, supersede the sample data with the data that you lot desire to plot in the chart. If you already have your data in another table, yous can copy the information from that table so paste information technology over the sample data. See the following table for guidelines on how to adapt the data to fit your chart type.
For this chart type
Arrange the data
Area, bar, cavalcade, doughnut, line, radar, or surface nautical chart
In columns or rows, every bit in the post-obit examples:
Series 1
Serial ii
Category A
10
12
Category B
11
14
Category C
9
15
or
Category A
Category B
Serial one
10
11
Serial 2
12
14
Bubble chart
In columns, putting x values in the first column and corresponding y values and bubble size values in adjacent columns, as in the following examples:
10-Values
Y-Value 1
Size one
0.7
two.vii
4
1.8
3.2
5
2.6
0.08
6
Pie chart
In 1 column or row of data and one column or row of data labels, as in the following examples:
Sales
1st Qtr
25
2nd Qtr
30
tertiary Qtr
45
or
1st Qtr
2nd Qtr
3rd Qtr
Sales
25
xxx
45
Stock nautical chart
In columns or rows in the post-obit gild, using names or dates equally labels, equally in the following examples:
Open
High
Low
Shut
1/5/02
44
55
xi
25
i/6/02
25
57
12
38
or
1/5/02
i/6/02
Open
44
25
High
55
57
Low
11
12
Close
25
38
X Y (scatter) chart
In columns, putting ten values in the offset column and respective y values in adjacent columns, as in the following examples:
X-Values
Y-Value i
0.7
2.seven
one.8
3.2
2.6
0.08
or
X-Values
0.7
1.8
2.six
Y-Value 1
two.seven
3.2
0.08
-
To change the number of rows and columns that are included in the nautical chart, rest the pointer on the lower-correct corner of the selected information, so drag to select additional data. In the following example, the table is expanded to include additional categories and data series.

-
To see the results of your changes, switch dorsum to Word or PowerPoint.
Note:When you lot close the Give-and-take document or the PowerPoint presentation that contains the chart, the chart's Excel data table closes automatically.
After y'all create a nautical chart, you might want to change the way that table rows and columns are plotted in the chart. For example, your first version of a nautical chart might plot the rows of information from the table on the nautical chart'southward vertical (value) centrality, and the columns of data on the horizontal (category) axis. In the post-obit example, the chart emphasizes sales by instrument.

Notwithstanding, if you desire the nautical chart to emphasize the sales past month, you can reverse the way the chart is plotted.

-
On the View card, click Print Layout.
-
Click the nautical chart.
-
On the Charts tab, nether Data, click Plot series by row
 or Plot series by column
or Plot series by column  .
.
If Switch Plot is non available
Switch Plot is available only when the chart'due south Excel information tabular array is open and only for certain chart types.
-
Click the chart.
-
On the Charts tab, under Data, click the arrow next to Edit, and and then click Edit Data in Excel.

-
-
On the View menu, click Print Layout.
-
Click the chart.
-
On the Charts tab, under Nautical chart Quick Layouts, click the layout that you want.
To see more layouts, point to a layout, and then click
 .
.To immediately undo a quick layout that you applied, press
 + Z .
+ Z .
Chart styles are a prepare of complementary colors and effects that you can apply to your chart. When you select a chart style, your changes affect the whole chart.
-
On the View carte du jour, click Print Layout.
-
Click the chart.
-
On the Charts tab, nether Chart Styles, click the style that you desire.
To see more styles, point to a mode, and then click
 .
.To immediately undo a way that you applied, press
 + Z .
+ Z .
-
On the View menu, click Impress Layout.
-
Click the chart, and then click the Chart Layout tab.
-
Under Labels, click Chart Title, and so click the i that you want.
-
Select the text in the Nautical chart Title box, and then type a chart championship.
See also
Update the information in an existing chart
Available nautical chart types in Office

Create a chart
Yous tin create a nautical chart for your data in Excel for the spider web. Depending on the data y'all have, you can create a column, line, pie, bar, surface area, scatter, or radar nautical chart.
-
Click anywhere in the data for which yous desire to create a chart.
To plot specific data into a chart, you tin can also select the information.
-
SelectInsert > Charts > and the chart type you desire.

-
On the carte du jour that opens, select the option you want. Hover over a chart to learn more nearly it.
Tip:Your choice isn't applied until you pick an option from a Charts command menu. Consider reviewing several chart types: as you lot point to carte items, summaries announced next to them to assist yous decide.
-
To edit the chart (titles, legends, data labels), select the Chart tab and and then select Format.
-
In the Chart pane, adjust the setting equally needed. Yous tin customize settings for the chart's title, legend, centrality titles, series titles, and more.

Available chart types
It's a good idea to review your data and make up one's mind what type of chart would work best. The available types are listed below.
Data that'due south arranged in columns or rows on a worksheet can exist plotted in a column chart. A column chart typically displays categories along the horizontal centrality and values along the vertical axis, like shown in this nautical chart:
Types of column charts
-
Clustered columnA clustered column nautical chart shows values in 2-D columns. Use this nautical chart when you have categories that represent:
-
Ranges of values (for example, item counts).
-
Specific scale arrangements (for instance, a Likert scale with entries, like strongly concur, agree, neutral, disagree, strongly disagree).
-
Names that are not in any specific order (for instance, detail names, geographic names, or the names of people).
-
-
Stacked column A stacked column nautical chart shows values in ii-D stacked columns. Apply this chart when you have multiple data series and you desire to emphasize the full.
-
100% stacked columnA 100% stacked column chart shows values in 2-D columns that are stacked to stand for 100%. Use this chart when you have 2 or more data series and you want to emphasize the contributions to the whole, specially if the total is the same for each category.
Data that is arranged in columns or rows on a worksheet can exist plotted in a line chart. In a line chart, category information is distributed evenly along the horizontal axis, and all value information is distributed evenly along the vertical axis. Line charts can prove continuous data over fourth dimension on an evenly scaled axis, and are therefore ideal for showing trends in information at equal intervals, like months, quarters, or fiscal years.
Types of line charts
-
Line and line with markersShown with or without markers to indicate individual data values, line charts can bear witness trends over time or evenly spaced categories, especially when you have many data points and the order in which they are presented is important. If there are many categories or the values are guess, utilize a line chart without markers.
-
Stacked line and stacked line with markersShown with or without markers to indicate individual data values, stacked line charts can show the trend of the contribution of each value over time or evenly spaced categories.
-
100% stacked line and 100% stacked line with markersShown with or without markers to point individual information values, 100% stacked line charts tin show the trend of the pct each value contributes over time or evenly spaced categories. If there are many categories or the values are gauge, utilise a 100% stacked line chart without markers.
Notes:
-
Line charts work best when you have multiple data series in your nautical chart—if you only have one data serial, consider using a scatter chart instead.
-
Stacked line charts add together the data, which might not be the result you desire. It might not be easy to see that the lines are stacked, so consider using a different line chart blazon or a stacked area chart instead.
-
Data that is bundled in ane column or row on a worksheet can be plotted in a pie chart. Pie charts show the size of items in 1 data series, proportional to the sum of the items. The data points in a pie chart are shown as a percentage of the whole pie.
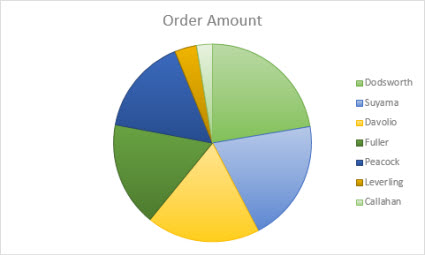
Consider using a pie chart when:
-
You have only one data serial.
-
None of the values in your data are negative.
-
Almost none of the values in your data are zip values.
-
You have no more than than seven categories, all of which represent parts of the whole pie.
Data that is arranged in columns or rows just on a worksheet can exist plotted in a doughnut chart. Like a pie chart, a doughnut nautical chart shows the relationship of parts to a whole, but it can contain more than 1 data series.
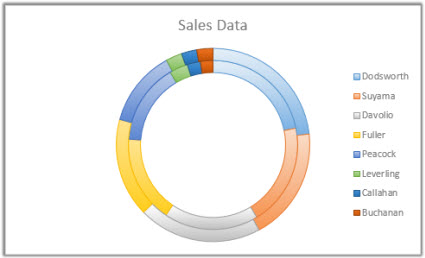
Tip:Doughnut charts are non like shooting fish in a barrel to read. You may want to use a stacked column or stacked bar chart instead.
Information that is arranged in columns or rows on a worksheet can exist plotted in a bar nautical chart. Bar charts illustrate comparisons amid individual items. In a bar chart, the categories are typically organized forth the vertical axis, and the values along the horizontal axis.
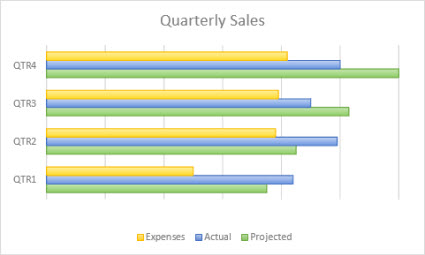
Consider using a bar chart when:
-
The axis labels are long.
-
The values that are shown are durations.
Types of bar charts
-
ClusteredA clustered bar chart shows bars in 2-D format.
-
Stacked barStacked bar charts show the human relationship of individual items to the whole in two-D bars
-
100% stackedA 100% stacked bar shows 2-D bars that compare the percentage that each value contributes to a total across categories.
Information that is arranged in columns or rows on a worksheet tin exist plotted in an area chart. Area charts can be used to plot change over fourth dimension and draw attention to the full value beyond a trend. Past showing the sum of the plotted values, an area chart too shows the relationship of parts to a whole.
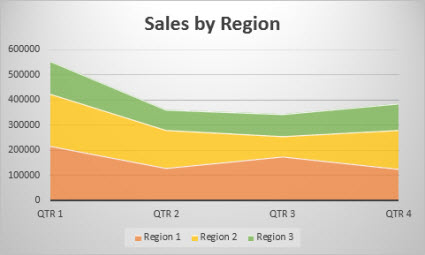
Types of area charts
-
AreaShown in 2-D format, area charts show the trend of values over time or other category data. As a dominion, consider using a line chart instead of a non-stacked area nautical chart, because data from one series tin exist hidden backside data from some other series.
-
Stacked areaStacked area charts show the trend of the contribution of each value over fourth dimension or other category data in ii-D format.
-
100% stacked100% stacked expanse charts evidence the trend of the percentage that each value contributes over time or other category data.
Data that is bundled in columns and rows on a worksheet tin be plotted in an scatter chart. Place the x values in i row or column, and so enter the corresponding y values in the adjacent rows or columns.
A scatter nautical chart has two value axes: a horizontal (ten) and a vertical (y) value centrality. Information technology combines x and y values into unmarried information points and shows them in irregular intervals, or clusters. Scatter charts are typically used for showing and comparing numeric values, like scientific, statistical, and engineering information.
Consider using a scatter chart when:
-
You desire to change the scale of the horizontal axis.
-
You desire to make that axis a logarithmic scale.
-
Values for horizontal centrality are not evenly spaced.
-
In that location are many data points on the horizontal axis.
-
You want to adjust the independent centrality scales of a besprinkle chart to reveal more information about data that includes pairs or grouped sets of values.
-
You want to show similarities between big sets of information instead of differences between data points.
-
You want to compare many data points without regard to time — the more than data that you include in a besprinkle chart, the better the comparisons you can make.
Types of scatter charts
-
BesprinkleThis nautical chart shows data points without connecting lines to compare pairs of values.
-
Scatter with polish lines and markers and scatter with smooth linesThis nautical chart shows a smoothen curve that connects the data points. Polish lines can be shown with or without markers. Employ a smooth line without markers if at that place are many information points.
-
Scatter with straight lines and markers and besprinkle with straight linesThis nautical chart shows straight connecting lines between data points. Directly lines tin be shown with or without markers.
Data that is arranged in columns or rows on a worksheet can be plotted in a radar chart. Radar charts compare the aggregate values of several data serial.
Type of radar charts
-
Radar and radar with markers With or without markers for individual data points, radar charts testify changes in values relative to a center point.
-
Filled radarIn a filled radar chart, the surface area covered by a data serial is filled with a color.
Add together or edit a chart title
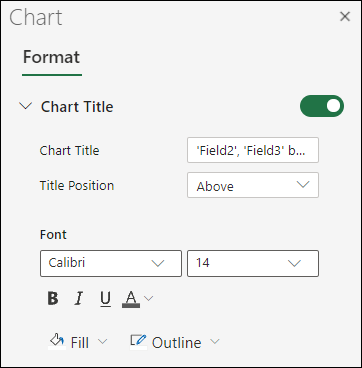
You tin add together or edit a chart title, customize its look, and include information technology on the chart.
-
Click anywhere in the chart to show the Chart tab on the ribbon.
-
Click Formatto open the chart formatting options.

-
In the Nautical chart pane, expand theChart Title section.
-
Add or edit the Chart Championship to come across your needs.
-
Use the switch to hide the title if you don't desire your chart to evidence a championship.
Add axis titles to improve chart readability
Adding titles to the horizontal and vertical axes in charts that take axes can make them easier to read. You can't add centrality titles to charts that don't have axes, such as pie and doughnut charts.
Much like chart titles, axis titles help the people who view the chart empathise what the data is about.
-
Click anywhere in the chart to bear witness the Chart tab on the ribbon.
-
Click Formatto open the nautical chart formatting options.

-
In the Chart pane, expand the Horizontal Centrality or Vertical Axissection.
-
Add together or edit the Horizontal Axis or Vertical Centrality options to meet your needs.
-
Aggrandize the Centrality Title.

-
Modify the Axis Championship and alter the formatting.
-
Use the switch to show or hide the title.
Modify the centrality labels
Axis labels are shown below the horizontal axis and next to the vertical axis. Your chart uses text in the source information for these axis labels.
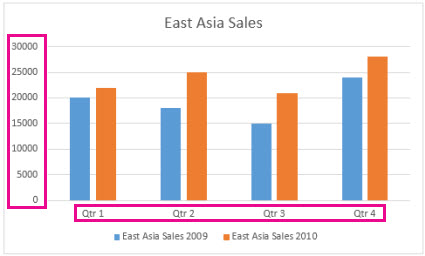
To change the text of the category labels on the horizontal or vertical axis:
-
Click the jail cell which has the label text you want to change.
-
Type the text you desire and press Enter.
The centrality labels in the chart are automatically updated with the new text.
Tip:Axis labels are dissimilar from axis titles you lot can add to describe what is shown on the axes. Axis titles aren't automatically shown in a chart.
Remove the axis labels
To remove labels on the horizontal or vertical axis:
-
Click anywhere in the nautical chart to show the Chart tab on the ribbon.
-
Click Formatto open up the chart formatting options.

-
In the Chart pane, expand the Horizontal Centrality or Vertical Centralitydepartment.

-
From the dropdown box for Characterization Position, select None to prevent the labels from showing on the nautical chart.

Need more help?
You can ever inquire an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.
Source: https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/office/create-a-chart-from-start-to-finish-0baf399e-dd61-4e18-8a73-b3fd5d5680c2
Posted by: taorminapricandere.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Use Excel To Make A Graph"
Post a Comment