Which Layer Of Skin Contains Sweat Glands
Overview
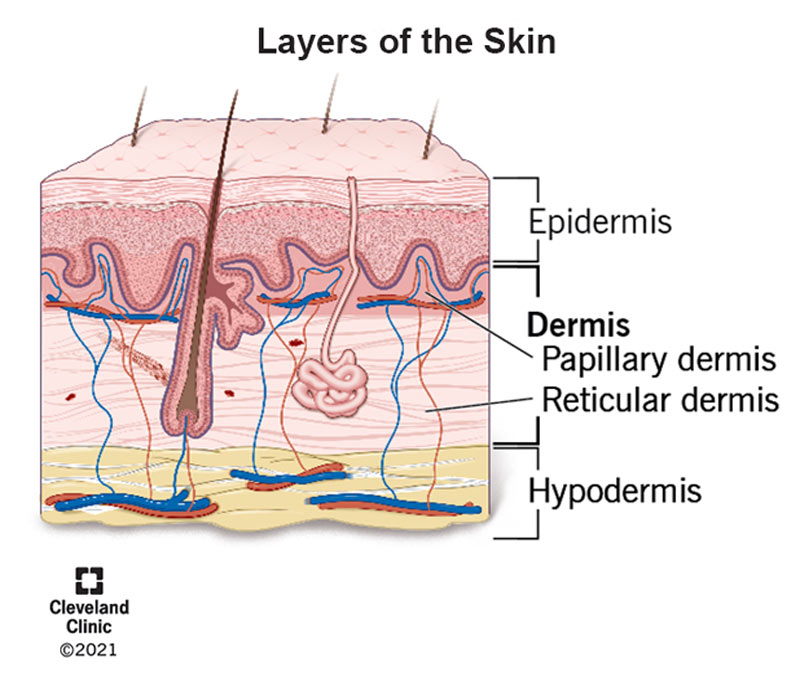
What is the dermis layer?
Your skin has three primary layers, and the dermis (corium) is the heart layer of skin in your body. The other two layers of skin are your epidermis and hypodermis. Your dermis layer consists of two layers of its own.
Corium is another name for the dermis. Corium is a Latin word that means "leather" or "pare."
What are the 2 layers of the dermis?
Your dermis consists of two layers:
- Reticular dermis: The reticular layer is the lesser layer of your dermis. It's thick, and it contains blood vessels, glands, hair follicles, lymphatics, fretfulness and fat cells. A net-similar construction of elastin fibers and collagen fibers surrounds the reticular dermis. These fibers support your skin'south overall structure, also as permit information technology to motion and stretch.
- Papillary dermis: The papillary layer is the peak layer of your dermis. It's much thinner than the reticular dermis. Information technology consists of collagen fibers, fibroblast cells, fat cells, blood vessels (capillary loops), nerve fibers, touch receptors (Meissner corpuscles) and cells that fight bacteria (phagocytes). The papillary dermis extends to the basement layer of the epidermis layer. They form a strong bond that connects like interlocking fingers.
What is the difference betwixt the dermis and the epidermis?
Your dermis and your epidermis are the top two layers of skin in your body. Your epidermis is the meridian layer, and your dermis is the middle layer. Your dermis exists between your epidermis and hypodermis.
Your epidermis is the thinnest layer of skin. It helps hydrate your trunk, produces new skin cells, protects your body from damage and makes melanin, which provides skin color.
While your epidermis is the thinnest layer of pare, your dermis is the thickest layer of skin. Your dermis contains collagen and elastin, which help make your dermis thick and supportive of your skin's overall structure.
All of your connective tissues, nerve endings, sweat glands, oil glands and hair follicles exist in your dermis.
Function
What are the functions of the dermis?
Each layer of your skin works together to protect your body. Your dermis has many additional functions, including:
- Supporting your epidermis: Your dermis's construction provides strength and flexibility, and claret vessels help maintain your epidermis past transporting nutrients.
- Feeling different sensations: Nerve endings in your dermis allow you to feel unlike sensations, similar force per unit area, pain, oestrus, cold and itchiness.
- Producing sweat: Your dermis contains sweat glands, which produce sweat when you're hot or experience stress. Sweat helps command your trunk temperature (thermoregulation).
- Keeping your peel moist: Your dermis contains sebaceous glands, which secrete an oily lubricant (sebum) that helps continue your skin and hair hydrated and shiny.
- Producing pilus: Your dermis contains hair follicles, which produce hair all over your skin, except the palms of your hands and the soles of your anxiety.
How does the dermis help with other organs?
Together with your other layers of peel, your dermis protects your skeletal system, organs, muscles and tissues from harm.
Anatomy
Where is the dermis located?
Your dermis is the middle layer of your skin, located between your epidermis (top layer) and hypodermis (bottom layer) in your pare.
What is the dermis's structure?
Your dermis consists of two layers — the reticular dermis and the papillary dermis.
How big is the dermis?
Your dermis varies in thickness beyond your torso. It'south thinnest over your eyelids, where it's 0.6 millimeters thick, and it'due south thickest over your back, where information technology'due south four millimeters thick.
What is the dermis made of?
Your dermis contains tissues with a lot of blood vessels that also include:
- Collagen.
- Elastin.
- A clear, gel-like fluid that fills the space between your cells and your fibers (ground substance).
- Diverse glands, including sweat glands and sebaceous glands.
- Pilus follicles.
Conditions and Disorders
What are atmospheric condition and disorders that affect the dermis?
Some conditions and disorders that affect your dermis include:
- Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.
- Hives (urticaria).
- Marfan syndrome.
- Primary dermal melanoma.
- Solar elastosis.
- Systemic sclerosis.
- Tumors.
What are mutual signs or symptoms of dermis conditions?
Some mutual signs or symptoms of weather that can touch your dermis include:
- Blood or another fluid leaking into your tissue from your arteries, arterioles, capillaries, tubes, venules or veins (extravasation).
- Changes in your basic, eyes, lungs, skin, heart and blood vessels.
- Dark, itchy patches of skin.
- Excessive bruising.
- Overly flexible joints (hypermobility).
- Soft skin that's thinner and stretches more than normal.
- Bloated tissue.
- Welts.
What are some common tests to check the health of the dermis?
- Genetic testing: The near mutual way to identify some weather condition is to await for a faulty cistron.
- Biopsy: Your healthcare provider will remove a sample of peel from your body and examine it under a microscope to look for diseases, infections or cancer.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) browse: An MRI can scan check for melanoma tumors in your brain or spinal cord.
- Positron emission tomography (PET) browse: A PET scan can cheque for melanoma in lymph nodes and other parts of your body that are further from the original melanoma spot in your skin.
What are common treatments for the dermis?
Some common treatments for conditions that touch your dermis include:
- Corticosteroids. Corticosteroids reduce inflammation and tissue damage.
- Pare grafts. Peel grafts treat damaged or missing skin that can't heal on its own. Skin grafts help people with deep peel damage or loss from burns, infections and ulcers.
- Skin substitutes. Peel substitutes include cells or tissue taken from another person (allograft), cells or tissue taken from an beast (xenograft) or peel made from nonbiological molecules and polymers (synthetic pare). Skin substitutes assistance people with deep skin wounds or atmospheric condition, including burns and infections.
Care
Simple lifestyle tips to proceed the dermis salubrious.
The following lifestyle tips assistance proceed your dermis salubrious:
- Establish a skincare routine. Drink at to the lowest degree eight spectacles of h2o each 24-hour interval, use mild soaps and cleansers, and moisturize your skin. Follow your healthcare professional's recommendations for keeping your dermis good for you.
- Properly care for your wounds. Launder pocket-sized open up wounds with clean running water and soap to preclude infections. And so, use a cotton swab to employ a small amount of petroleum jelly (Vaseline™) or skincare ointment (Aquaphor™) over the wound, and encompass it with an adhesive bandage to prevent dirt or bacteria from entering the area.
- Avert sunday harm. Long exposure to the lord's day amercement your peel. Use sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 and wear protective wearable.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Your dermis is the middle layer of skin in your body. It has many of import functions, including protecting your body from the outside earth, supporting your epidermis, feeling different sensations and producing sweat. Information technology's important to accept care of your dermis. You lot can help take care of your dermis past drinking plenty of h2o, properly treating your wounds and avoiding sun damage.
Source: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/22357-dermis
Posted by: taorminapricandere.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Layer Of Skin Contains Sweat Glands"
Post a Comment